A Diamond is composed of compressed carbon atoms that formed into a repeating geometric pattern millions of years ago under the earth's surface. Fancy color Diamonds are the natural phenomenon where another element was introduced during the Diamond's formation, allowing for the presence of a beautiful color. Only 1 in every 1,000 carats of Diamonds mined each year is colored, and the rarer colors occur even less frequently - 1 in every 10,000 carats mined. This quantity is steadily shrinking although colorless Diamonds still exist readily in nature in large quantities.
In order to classify diamonds as natural fancy color Diamonds, they are certified in a gemological institute such as GIA, HRD, or IGI according to their attributes. They are only considered natural if their color came from Nature and not from a lab.

The 12 different main colors of Natural Fancy Colored Diamonds
From left to right - Yellow, Pink, Blue, Green, Orange, Brown, Violet, Gray, Purple, Red, Fancy Black, and Fancy White
Once a stone has been graded and certified, the natural color Diamond will have its own personal ID, which includes an ID number, its measurements, weight, shape, clarity, polish, symmetry and fluorescence. These categories are usually classified as the 4Cs of Diamonds - Color, Cut, Clarity and Carat weight, though shape and fluorescence are often additional important factors. Depending on how they exhibit these qualities, fancy color Diamonds will be valued differently for sales purposes.
Color
The most important characteristic in fancy color Diamonds is their beautiful color. Natural fancy color Diamonds appear as one primary color. However, most of the natural fancy color diamonds that are mined are generally not a pure color. Some Diamonds have a combination of two, three, and sometimes even four colors that appear in the stone. The presence of color and the intensity of its shine is specifically what increases the value of the diamonds, as some exhibit the color more faintly than others.
The color of the Diamonds is defined by a number of characteristics. Different compound elements in the stones produce the exquisite color in fancy color Diamonds. Without the compound elements, the Diamond would appear as a regular, colorless Diamond. A color Diamond is considered the most beautiful when its exhibits a strong presence of color in the Diamond that is easily identifiable to the human eye. That is not to say that some people don't also consider a lighter colored stone to be beautiful as well. In fact, some people prefer lighter colored stones. However, the more vivid stones are more valuable. By definition, a perfect colorless Diamond has no additional chemical traits, a structurally perfect form, and absolutely no color at all. These requirements are hard to obtain and they also define a Diamond as incredibly valuable.

Pure, Natural Fancy Colored Diamonds
From left to right: Fancy Vivid Pink, Fancy Vivid Green, Fancy Vivid Blue, Fancy Vivid Yellow, and Fancy Vivid Purple
The various Diamond colors found are blue, pink, yellow, orange, green, brown, grey, black, purple, violet, white, and the rarest red. However, as rare as color diamonds are, pure or single color stones are even more difficult to acquire. Most color Diamonds are combinations of certain colors, with secondary hues or overtones.
Cut
Fancy loose color Diamonds are polished in a different manner than colorless Diamonds. This is done in order to emphasize the Diamond's color as much as possible. By definition, the cut is the naturally prearranged faceted arrangements of the Diamond. In the industry, the 'make' of the Diamond is the degree of how professionally the faceted arrangement is created, since it is through the cut that the finished product is made.
Without the sparkle and shine one expects to see, a Diamond would appear as just another nice looking gemstone. Granted, the color and clarity of the Diamond are both major contributors to the brilliance - but the cut is precisely what changes the stone from a shimmer to shine. No two Diamond roughs will be exactly identical. The challenge of the Diamond cut is the technique of how to derive the best finished product from the Diamond's rough.

White Diamond on the Polishing Wheel
People often confuse the cut with the shape of a stone. However, even though they are related, they are not at all the same. The Diamond cut refers to the style used to form the stone regardless of the Diamonds shape. The styles are different forms of symmetry, polish, and geometric proportioning between the Diamond's many facets, otherwise known as the make. Any specific Diamond shape can have more than one different Diamond cut. The styles are in every sense of the words both a science and an art.

Two Pear-Shaped Diamonds, the Left has a Round-Edge Fancy Cut, and the Stone to the Right a Step Cut

From Left to Right, a Round-Edge Fancy, a Step Cut, a Modified Cut, and a Mixed Cut
The goal for a fancy colored Diamond is quite different than that for a colorless stone. The goal is to increase the color intensity and improve the color saturation. Therefore, fancy colored Diamonds often contain asymmetric, elongated facets. This helps to control the light that reflects through the stone. Since the color is actually the most important attribute of a fancy colored diamond, cutting it in a way that causes this affect can only help increase the value of the stone.
Clarity
Usually, an untrained person might be able to differentiate two of the four parameters: (carat) weight and color. The other two parameters, clarity and cut, are more complex and require expertise.
Most Diamonds have certain imperfections from the volcanic rock where the Diamond formed. The imperfections are natural internal occurrences called inclusions, or external occurrences called blemishes. Clarity, therefore, refers to the nature, color, number and size of such inclusions and/or blemishes.
The Diamond's Clarity grade is determined not by the naked eye, but by the stone's appearance when viewed under a 10x power magnification, and by an experienced grader. Grades FL (flawless) through SI (some inclusions), which are not normally visible; affect the value of the Diamond but not its external appearance when viewed with the naked eye.
Darker inclusions found in white or colorless diamonds will have the greatest affect on a lower diamond clarity grading. In fancy color Diamonds, lighter inclusions are the cause of significant drop in clarity grade.

The 69.68 ct. Graff Excelsior, One of the World's Most Beautiful Diamonds
Carat
A carat refers to the unit of measurement that is used to describe the weight of the Diamond. The carat weight is not the technical metric weight and size of the Diamond, although the two measurements are definitely related.
The appearance of the Diamond's size will be significantly affected by the piece of jewelry selected and the setting in which it is placed. Also, certain shapes tend to look larger than other shapes, despite the fact that they might be a lower carat weight. For example, an oval Diamond's taller appearance will seem larger than a round shape. A marquise shape, due to its elongation, also seems to have a larger appearance than shapes that are not elongated.
The two stones below look quite different in size as a result of their shapes, but there really is only 28 points between the two!

3.11 Carat, Fancy Deep Grayish Blue Cushion Cut, and a 2.83 Carat, Fancy Grayish Blue Emerald Cut
Many characteristics affect the appearance of the stone. For example, a colorless Diamond that is cut very well, in a way that light can quickly pass through, will actually appear slightly bigger from the sparkle. Fancy colored Diamonds work the same way, with the difference that the cut should also cause the light to remain within the stone for as long as possible, to help accentuate the color.
Shape
The classification of a Diamond rough into the shape in which it will be cut is a complicated, intricate process. In their rough form, an untrained individual would have no scientific way of deducing into what shape the stone will be most ideally cut. Regardless of the size of the rough, each Diamond must be analyzed on its own by a professional to assess the ideal shape into which the Diamond should be cut.

The most commonly found shapes of color Diamonds are radiant and cushion, although there is a plethora of diamonds available in the other shapes. Radiant and cushion shapes, are known to absorb the light and therefore often grade very well on the GIA intensity scale. They are therefore considered a 'safe bet' when it comes to shaping the stones. In fact, as a result of the facet arrangements in these shapes, imperfections may be less noticeable as well. Shapes like the emerald and princess cuts hold the light the least, which is why they are a rarer find in the world of color Diamonds. When a color diamond is cut into a shape that doesn't keep the light in as well, it is usually because the color from the Diamond rough was so vibrant that it would not have been lost from the shaping process. However, if the cutter manages to create a fancy colored emerald cut Diamond with a high level of color intensity, the value of the stone will increase considerably.

Emerald shape Pink diamonds
Fluorescence
Diamond fluorescence is in essence the inclusion of elements such as nitrogen, boron, or aluminum that cause a magnificent glow. Depending on the fancy color diamond's composition, the fluorescence can appear in a number of different shades or colors such as blue, yellow, white, orange, green, or pink. In colorless Diamonds, fluorescence will generally appear only in a yellow or blue tint. Only about 35% of stones available today actually have fluorescence, and only about 10% of those have enough fluorescence to cause a change of appearance under ultraviolet light.
 Very Strong Green Fluorescence
Very Strong Green Fluorescence
 Strong White Fluorescence
Strong White Fluorescence
Since diamond fluorescence can glow at different levels, the GIA developed a grading scale to measure the strength of the illumination:
- None
- Faint
- Medium
- Strong
- Very Strong

Left to Right: Faint, Medium Blue, Strong Blue, Very Strong Blue Fluorescence
The Effects of Diamond Fluorescence
Many Diamond retailers will tell you that fluorescence is known as a negative trait in the industry. As a result, the price of Diamonds that contain diamond fluorescence is usually slightly lower due to the 'reduced' quality of the stone. However, there are two points that must be considered about this truly amazing phenomenon: First, Diamond fluorescence can only be distinguished by the naked eye under ultra violet lighting. Even a very strong fluorescence will appear extremely faint under direct sunlight. Second, Depending on the color of the stone and the color of diamond fluorescence, it can sometimes even improve the color of the stone.
Diamond fluorescence might be an excellent way to get your hands on a beautiful stone that would have been above your price range. As a result of the fluorescence, the cost will most likely be reduced because of the popular opinion about fluorescence. Depending on the intensity of the fluorescence, you might be able to negotiate more with the price.
In the Industry
The question of whether Diamond fluorescence is a positive or negative trait is actually quite a debated subject. There have been many different opinions on the matter. Whether fluorescence will be considered a positive trait or not, will depend entirely on the color of the Diamond and the color of the fluorescence.
Not all Diamonds fluoresce, and ones that do can be measured. In general, the price of the Diamond will not be affected if it is graded a 'faint' fluorescence. It might be affected if the grade is 'medium', depending on the characteristics of the stone itself. However, if there is a 'strong' or 'very strong' presence in the stone, the price is likely to be reduced.
Finding a yellow Diamond with fluorescence is actually quite common. However, the illumination level is usually faint. When purchasing a yellow Diamond, ask the vendor what type of effect the fluorescence has on the stone's appearance. In certain cases it might not even be noticeable. In others, it can give the stone a slight brownish tint or even a milky appearance. The potential benefit is that if the fluorescence is not actually visible, you could acquire a stone that looks no different from one without fluorescence for a significantly reduced cost. Pink Diamonds, on the other hand, are quite difficult to find without fluorescence. In fact, since the addition is so common, especially in Argyle pink Diamonds, even a strong grade will generally not negatively impact the value of the stone. In general, a pure blue Diamond will not have any fluorescence at all. In the event that fluorescence is found, which often means that the Diamond color exhibits a greenish overtone, the fluorescence will usually not even be noticeable. Certain diamond fluorescence is considered extremely rare and actually considered a collector's items, for example, a red fluorescence.
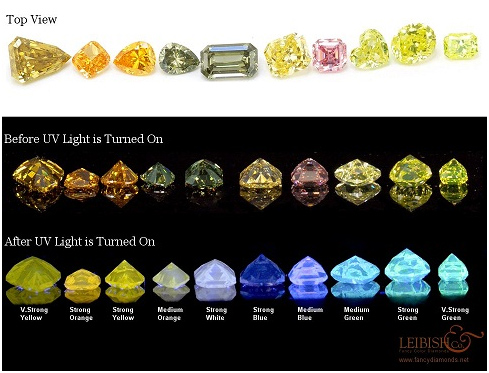
Fancy Color Diamond Fluoresence
From left to right: Fancy Deep Brownish Yellow, Fancy Vivid Yellow Orange, Fancy Vivid Yellow Orange, Fancy Deep Grayish Yellowish Green/Chameleon, Fancy Dark Gray Yellowish Green/Chameleon, Fancy Intense Yellow, Fancy Pink, Fancy Greenish Yellow, Fancy Intense Green Yellow, Fancy Intense Green Yellow.
|